Blue Light - is it bad for your skin?

Blue light is all around us and we’re exposed to it on a daily basis but the question you may be asking yourself is blue light your friend or foe? People are familiar with the artificial blue light from devices, but what are the other sources of blue light? What are the pros and cons? Our team of skin researchers are here to reveal the science behind blue light by separating fact from fiction.
Are there any benefits to the skin from blue light?
Blue light therapy, when administered by a skincare professional, is the only time it may be beneficial to the skin. Blue light is used as part of acne treatment through a mechanism of killing certain bacteria on the surface of the skin which contribute to acne.
What are the negative impacts to the skin?
Did you know that blue light makes up 30% of the rays from the sun while UV light only comprises 5% of sunlight?
Research shows that blue light from the sun negatively affects our skin. The blue light waves penetrate deeper into the skin than UVA and UVB radiation, affecting our cells in both the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin, causing longer term damage, deep lines, wrinkles, pigmentation, and sagging.
Blue light seriously impacts skin structures including fibroblasts, keratinocytes, melanocytes, and the protective lipid layer.
Fibroblasts and keratinocytes, are two of the most abundant cell types present in the skin. It has a variety of functions. They secrete collagen proteins that help maintain the structural framework of tissues. Blue light damages these skin cells, which results in the lines and wrinkles forming and accelerating skin ageing.
Melanocytes are another type of skin cell targeted by blue light. Melanocytes are a cell in the skin that produces and contains the pigment called melanin. They live in the layer of basal cells at the deepest part of the epidermis. When they are damaged, they cause discolouration, pigmentation, and brown spots.
Furthermore, blue light damages the lipid layers between skin cells. The lipid layers are the fatty compounds helping to control what goes in and out of your skin and protects skin from external aggressors like blue light. When the lipid layers are damaged it compromises the skin barrier function, causing skin to be red, reactive, and sensitive.
The impact of blue light to the skin is serious. Although, some blue light therapy may be used for a specific skin concern, there are still potential side effects. Blue light is certainly not your friend.
Blue light from the sun has a greater negative impact to the skin than UV rays. Discover more about blue light and how you can help protect your skin all year round from this external aggressor.
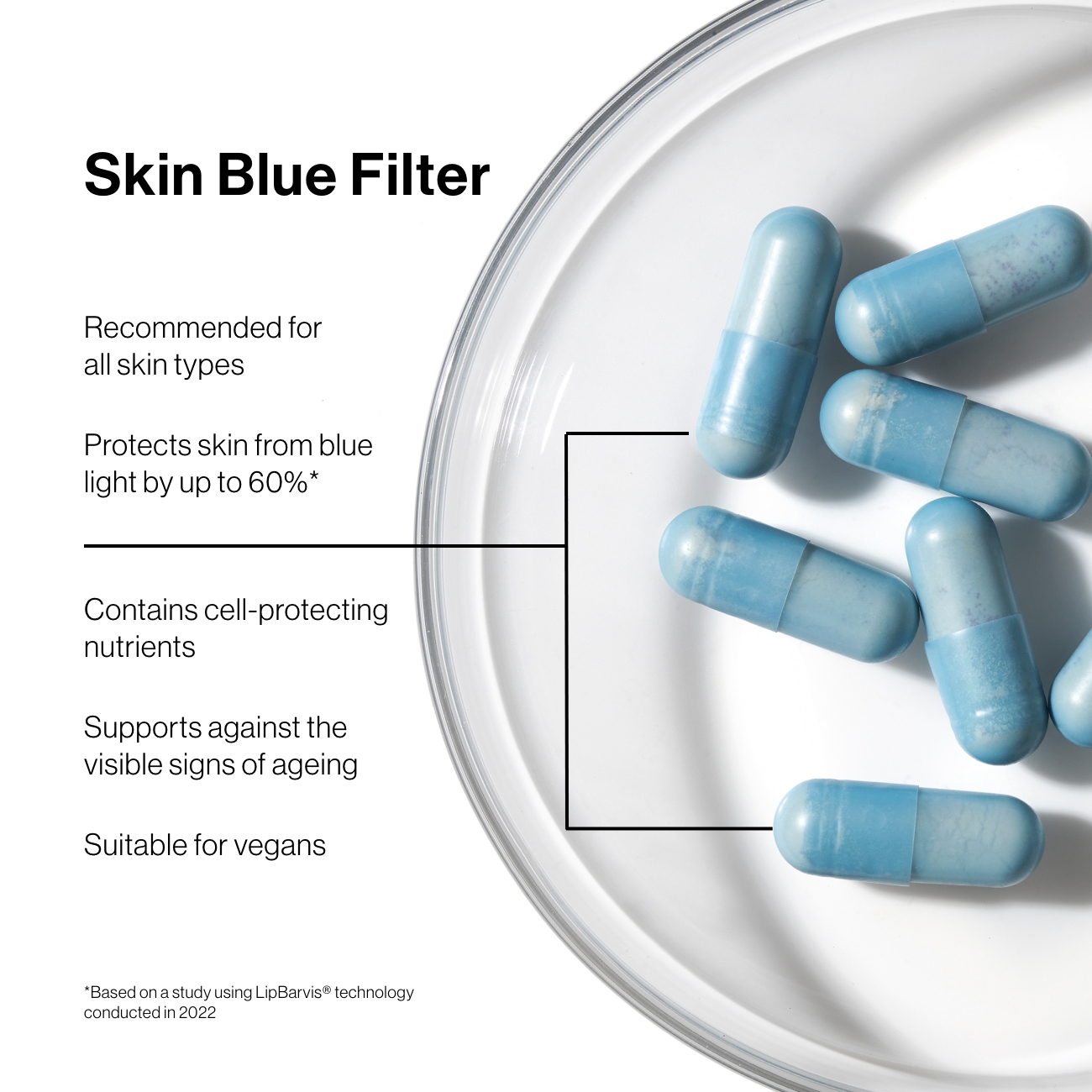
Our new blue light supplement shields skin from the impact of blue light by 60%*